Safety and PV systems

Let’s be absolutely clear –PV systems are safe
A large number of studies from renowned institutions such as the German organisation TÜV Rheinland, the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems, and the BRE National Solar Centre in the UK have already demonstrated in extensive investigations that photovoltaic systems are extremely safe. For example, analysis carried out by TÜV Rheinland in 2015 showed that just 0.016% of the 1.3 million systems installed before 2013 had been damaged by heat or fire. The British institution, BRE National Solar Centre, goes even further: by 2017, over 1 million PV systems had been installed in the UK, of which fewer than 0.006% had sustained heat or fire damage caused by the PV system.
The safety of PV systems continues to increase
When comparing these two studies, it is clear to see that PV systems are becoming increasingly safe over time. It should also be taken into account that the cases of damage demonstrated do not necessarily have to involve a fire. Heat damage, for example, includes instances of discolouration or the deformation of system components due to high heat generation. As yet there has not been a single demonstrable case in Germany where a member of the emergency services has been injured while tackling a fire as a result of a PV system.
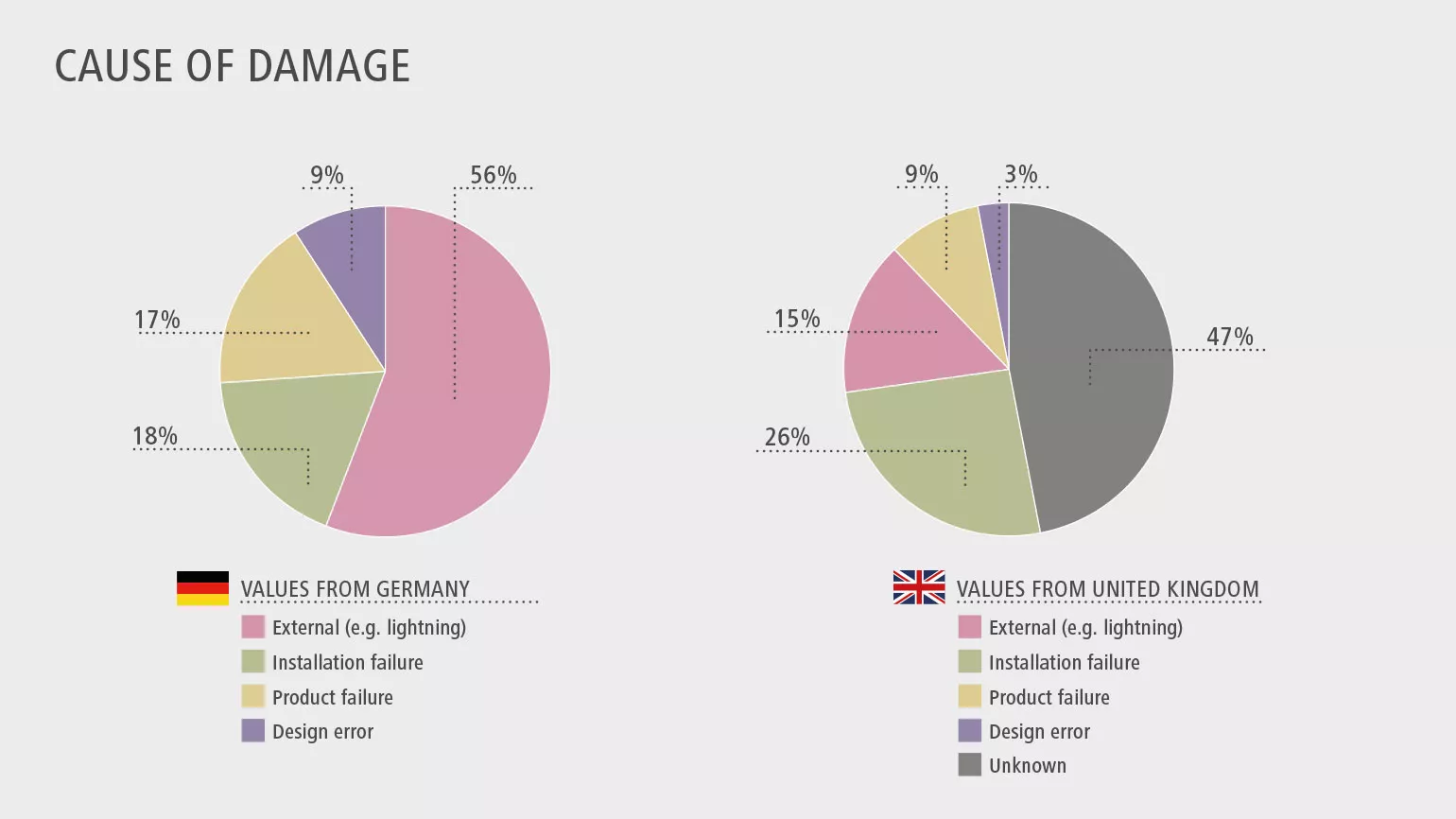
External influences and installation errors the main cause of fires
Both studies confirm that, in over 70% of cases involving heat or fire damage, external influences or installation errors were the main causes of fire. Faulty PV-system components were diagnosed as the cause of damage in just 17% (TÜV Rheinland) and 9% (BRE National Solar Centre) of cases.
Defective connectors can lead to electric arcs
If a PV system is not installed properly, electric arcs may be generated. In both studies, the use of DC plugs from different manufacturers was identified as the main cause of electric arcs. For this reason, installers must ensure that they always use plugs from one manufacturer, otherwise electric arcs may arise, resulting in heat or fire damage. The more contact points there are on a roof, the greater the likelihoodt hat an electrical arc will arise and this can increase the risk of fire.
Recommendations and measures for accident prevention
There are some very simple measures users can take to minimise the risk of a heat or fire-based accident:
- Intelligent system monitoring: the Fronius Solar.web online portal provides the perfect platform for a clear overview of all energy flows in the PV system. Should any deviations from normal operation occur, system operators can react quickly and restore the system to normal status.
- Daily and automated insulation monitoring: before the inverter begins feeding in, the insulation resistance is checked. If any irregularities are detected, the inverter will not start up and will inform the user that something is wrong. Monitoring also takes place during ongoing grid power feed operations. As soon as an irregularity is detected, the inverter switches off and issues an error code.
- Professional installation and start-up: the studies show that installation errors are among the main causes of damage. Fronius counteracts this by way of an extensive programme of education and training.
- Periodic maintenance and inspection: PV systems should also be regularly maintained and inspected by a professional.